
Your Tamworth Electrician is here to explain what a consumer unit is & how they work...
Despite every house having one many of us do still have this problem. Hopefully this might help you in your hour of need to get things up and running – and if not know when to contact us for help.
What is a consumer unit?
A consumer unit, also known as a fuse box or breaker box, is a crucial component of your home's electrical system. It distributes electricity to different circuits within your home and protects against electrical faults. Here's a straightforward guide to the anatomy of a consumer unit, explaining each device, its function, and how to control it:
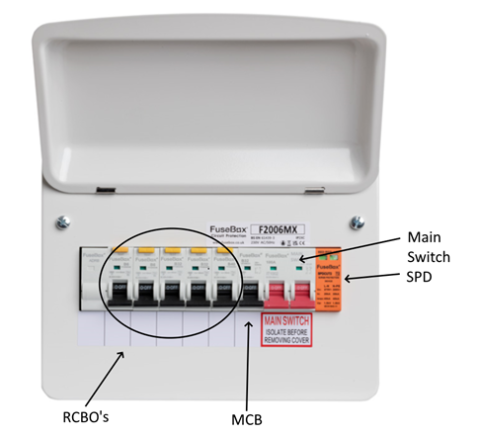
Main Switch: (RED)
The main switch serves as the primary disconnect for your home's electrical supply, ensuring safety during emergencies and maintenance. In modern consumer units, the main switch may include additional features like integrated RCD protection for the entire installation (see below).
Residual Current Devices (RCDs - Double width with small reset button)
Many consumer units have a main or dual RCD providing protection across multiple MCB circuits. RCDs are sensitive to small leakage currents, enhancing your safety by quickly disconnecting power if they detect any imbalance between Live and Neutral. All RCDs must cut power in less than 400 milliseconds to limit any serious harms from electric shocks.
Press the ‘Test’ button every 3 months to confirm its functioning correctly.
Individual circuits may be protected by either standard MCBs or RCBOs:
Mini Circuit Breaker (MCBs)
MCBs provide overcurrent protection – preventing damage to your cabling, sockets and other accessories. RCBOs provide both overcurrent protection and residual current protection in a single unit.
Each of these devices is dedicated to a specific circuit – sockets, cooker, lights etc
RCBOs (Residual Current Breakers with Overcurrent Protection):
RCBOs provide both overcurrent protection (similar to MCBs) and residual current protection (similar to RCDs) for individual circuits. They trip in the event of an overcurrent or a fault current to earth, ensuring enhanced safety for specific areas or appliances.
Press the ‘Test’ button every 3 months to confirm its functioning correctly.
Control:
Each MCB/RCBO has its own switch. To turn off power to a specific circuit or appliance, locate the corresponding RCBO and switch it to the "Off" position. If an MCB/RCBO trips, investigate and fix the issue before resetting it by moving the switch to the "On" position.
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs):
SPDs protect your home's electrical and electronic devices from voltage spikes caused by lightning strikes or other power surges. They divert excess voltage to the ground, preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
Important Safety Tips:
- Regular Checks: Include visual inspections of RCBOs, SPDs, and other components during routine checks to ensure they are in good condition.
- Testing: Periodically test the operation of RCDs and RCBOs as per the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Professional Installation: Consult a qualified electrician for the installation of RCBOs, SPDs, or any modifications to the consumer unit.
Hopefully this helps to get you up to speed with your consumer unit. If yours looks nothing like the above unit now is the time to get in touch about upgrading your consumer unit.
- Log in to post comments
